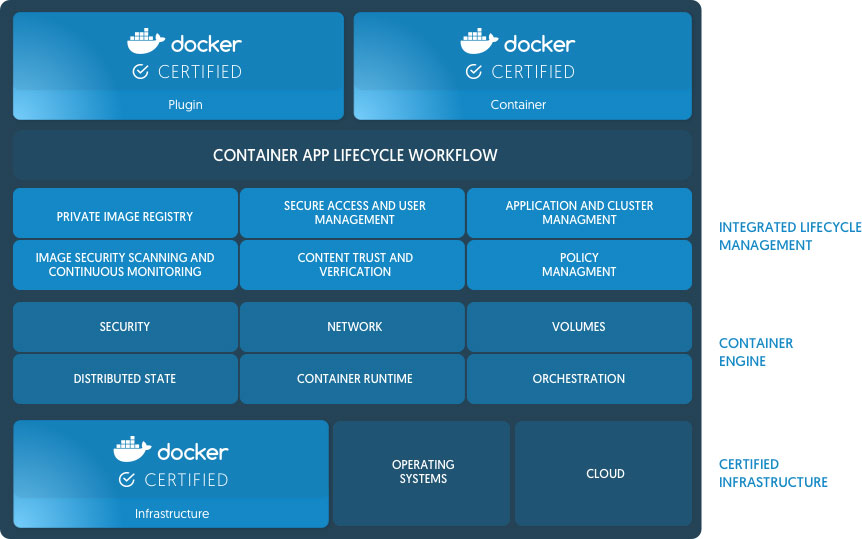
Docker Releases Enterprise Edition with Multi-Architecture and Multi-Tenant Support
On August 16, 2017 Docker announced the new release of Docker Enterprise Edition (EE). Docker EE is a Container-as-a-Service (CAAS) platform that provides a cross-platform, cross-architecture supply chain and deployment environment for software applications and microservices built to work in Windows, Linux and Cloud environments. The Docker container platform is integrated to the platform infrastructure to provide a native and optimized experience for the applications. Docker EE has the Docker tested and certified infrastructure, containers and plugins needed to run applications on Enterprise Platforms. The new Docker EE provides a container management platform that accommodates Windows, Linux and Mainframe apps and supports a broad range of infrastructure types.

Is Docker Perfect for Databases?
Docker – a Revolutionary Container Platform
Before going into the analysis, let’s have a brief idea about Containers and Docker. A Container is an executable package of software designed to provide an isolated environment for applications to run in a host server. They have all the necessary code, runtime, libraries etc. to provide a safe environment for the application software. Prominent enterprises like Uber, Facebook, Google etc are using Containers in a very high scale. Docker is a software container platform and is used to create container units on host machines. Many such units share the host’s OS, RAM, Processor and other resources. Disk usage is minimized by sharing filesystem layers and common files. Docker containers help in many aspects for Software Lifecycle, starting from development to deployment and implementation. It provides an agile continuous integration platform with isolated units for development teams, with development, test and production environments. It makes a server compatible for a wide variety of software applications that have different dependencies. Docker makes the host platform portable and distributed by virtue of its self sufficient and isolated container feature. All these come along with reduced need of computing power and space, since Docker Containers use the same Kernel in a host, rather than VMs using separate guest OS.
Read more